Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is not high cholesterol. In the old days it was also called hardening of the arteries and that is a good description of one of the signs. It refers to the build-up of plaques on the arterial walls, which can restrict blood flow. It's a chronic disease (a “syndrome”) that typically lasts until the person dies – sometimes decades after onset. The circulatory system has been inflamed. If you could see if, it would be a different color than healthy arteries. Fatty material (atheromas or atherosclerotic plaques) accumulate as patches. Anatomists describe tissue with atherosclerosis as looking like marbled meat – with streaks of fat visible. The elastin and collagen in the cardiovascular system have been attacked, altering the flexibility of the tissue. Healthy arteries are elastic. Toughened and partially blocked arteries restrict blood flow to tissue.
Arteriosclerosis and atherosclerosis are different but related conditions. Arteriosclerosis is a more general term for loss of elasticity in arteries and the word is usually used to describe the situation in small arteries only. When medium and large arteries get arteriosclerosis the situation is described as atherosclerosis.
In addition to being “hardened” these arteries permit less blood flow than healthy arteries do. The channel is narrower, meaning the heart has to pump harder to get the same blood flow through the tissue. The plaque – made of deposited cholesterol, calcium salts, collagen, dead cells, and other fatty materials, physically restricts blood flow.
A series of injuries
Looking at it as a chronic condition, atherosclerosis is a cumulative result of injuries sustained over the years. There are no symptoms until the disease has progressed so much that the patient can feel the numbness, ramping, or weakness in the extremities. High blood pressure, diabetes, and high levels of cholesterol in the blood contribute to these injuries. Atherosclerosis affects over half of Americans past age 60 and is the leading cause of death worldwide.
Any artery can be affected by atherosclerosis. If the arteries in and around the heart get it, the result is coronary heart disease. If the arteries that deliver blood 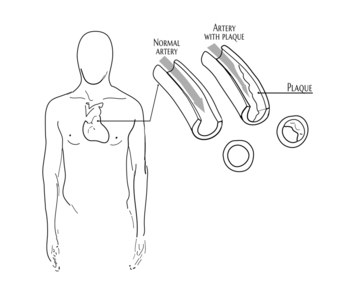 to the head - the carotid arteries - get atherosclerosis, the result is carotid artery disease, which is a major cause of stroke.
to the head - the carotid arteries - get atherosclerosis, the result is carotid artery disease, which is a major cause of stroke.
Coronary artery disease (CAD) - Atherosclerosis in the coronary arteries which are the arteries that bring blood to the heart. CAD happens when these arteries become hardened and narrowed. The hardening and narrowing of those arteries is a major risk for diseases include stroke, hypertensive heart disease, rheumatic heart disease, cardiomyopathy, heart arrhythmia, congenital heart disease, valvular heart disease, carditis, aortic aneurysms, peripheral artery disease, and venous thr factor for heart attack because if plaque breaks off and blocks a blood vessel, blood flow to the heart can be cut off.
CVD has been the leading cause of death in the United States each year for the past 100 years.
If atherosclerosis affects the renal arteries the result can be chronic kidney disease. If atherosclerosis affects the major arteries in the lower body (outside the head and heart), it is called peripheral arterial disease.
Statins reduce the rate of oxidation of LDL. This oxidation is suspected to play a role in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis The statins may also slow white blood cells' tendency to stick to the walls of blood vessels, and they might (this is more speculative) increase the formation of blood vessels. And the reduction in blood vessel inflammation statins are thought to lead to a lower risk of atherosclerosis. When blood lipid levels are lowered (from any means) atherosclerotic lesions can regress. Scientists have found evidence that taking statins leads to an increased rate of calcification and increaed density of plaques.
A thrombosis is a blood clot. It obstructs blood vessels. Atherothrombosis is when there is atherosclerosis with a clot on it.
Long Term
Atherosclerosis is a strong indicator of future coronary heart disease. Atherosclerosis is a condition that calls for long-term management. To prevent it or slow its progression, you should eat a healthy diet, not use tobacco, exercise, and keep your blood pressure under control. The idea behind statin therapy is that by targeting hypercholesterolemia medicine can prevent atherosclerosis. Monitoring cholesterol levels and addressing dyslipidemia is also an important part of prevention. If the atherosclerosis gets bad enough the risk for heart attack and stroke goes up considerably.
Hormone replacement therapy given to women soon after menopause has been shown to provide cardiovascular benefits but there are downsides to this therapy and it is not as popular as it once was.